China-based purveyors of SMS phishing kits are having fun with exceptional success changing phished fee card knowledge into cell wallets from Apple and Google. Till not too long ago, the so-called “Smishing Triad” primarily impersonated toll street operators and delivery corporations. However consultants say these teams are actually instantly focusing on prospects of worldwide monetary establishments, whereas dramatically increasing their cybercrime infrastructure and help workers.

A picture of an iPhone machine farm shared on Telegram by one of many Smishing Triad members. Picture: Prodaft.
Should you personal a cell machine, the probabilities are glorious that in some unspecified time in the future up to now two years you’ve acquired at the very least one on the spot message that warns of a delinquent toll street payment, or a wayward package deal from the U.S. Postal Service (USPS). Those that click on the promoted hyperlink are dropped at an internet site that spoofs the USPS or an area toll street operator and asks for fee card info.
The location will then complain that the customer’s financial institution must “confirm” the transaction by sending a one-time code by way of SMS. In actuality, the financial institution is sending that code to the cell quantity on file for his or her buyer as a result of the fraudsters have simply tried to enroll that sufferer’s card particulars right into a cell pockets.
If the customer provides that one-time code, their fee card is then added to a brand new cell pockets on an Apple or Google machine that’s bodily managed by the phishers. The phishing gangs usually load multiple stolen cards to digital wallets on a single Apple or Android device, after which promote these telephones in bulk to scammers who use them for fraudulent e-commerce and tap-to-pay transactions.
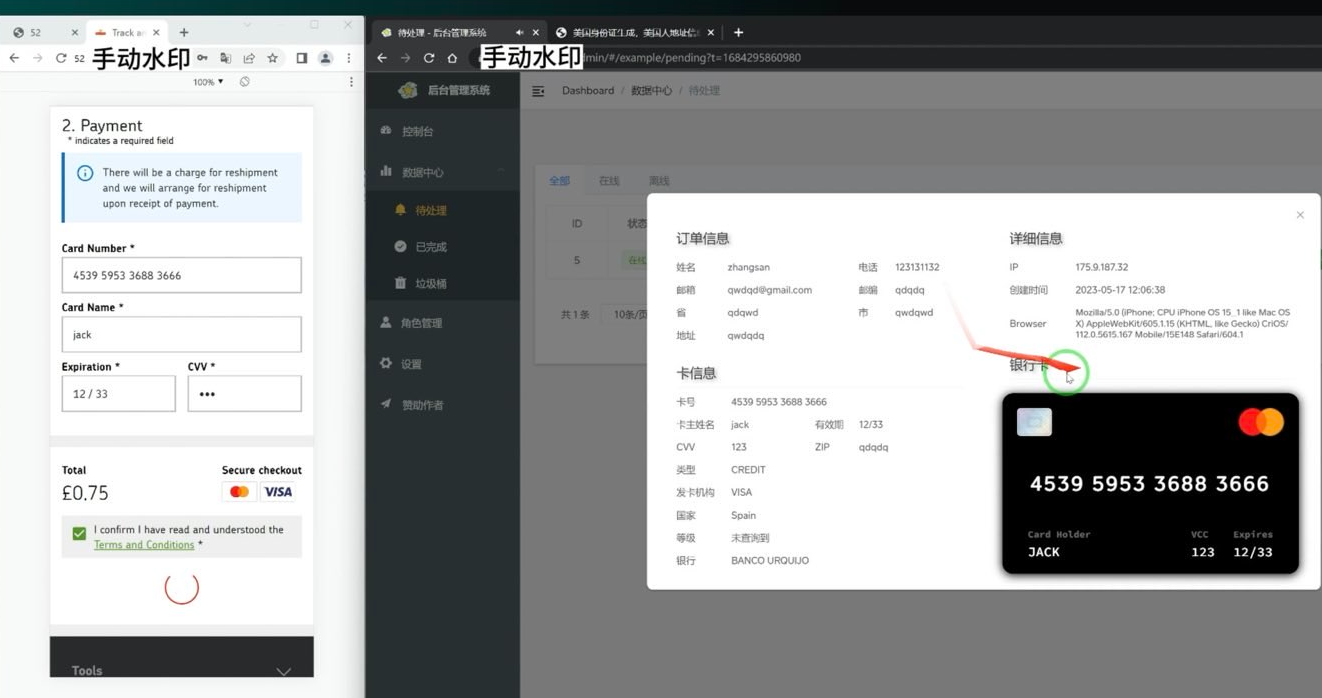
A screenshot of the executive panel for a smishing package. On the left is the (check) knowledge entered on the phishing web site. On the fitting we are able to see the phishing package has superimposed the equipped card quantity onto a picture of a fee card. When the phishing package scans that created card picture into Apple or Google Pay, it triggers the sufferer’s financial institution to ship a one-time code. Picture: Ford Merrill.
The moniker “Smishing Triad” comes from Resecurity, which was amongst the first to report in August 2023 on the emergence of three distinct cell phishing teams primarily based in China that appeared to share some infrastructure and modern phishing strategies. However it’s a little bit of a misnomer as a result of the phishing lures blasted out by these teams should not SMS or textual content messages within the typical sense.
Moderately, they’re despatched by way of iMessage to Apple machine customers, and by way of RCS on Google Android gadgets. Thus, the missives bypass the cell phone networks completely and revel in close to 100% supply charge (at the very least till Apple and Google droop the spammy accounts).
In a report printed on March 24, the Swiss risk intelligence agency Prodaft detailed the fast tempo of innovation coming from the Smishing Triad, which it characterizes as a loosely federated group of Chinese language phishing-as-a-service operators with names like Darcula, Lighthouse, and the Xinxin Group.
Prodaft mentioned they’re seeing a major shift within the underground economic system, notably amongst Chinese language-speaking risk actors who’ve traditionally operated within the shadows in comparison with their Russian-speaking counterparts.
“Chinese language-speaking actors are introducing modern and cost-effective programs, enabling them to focus on bigger consumer bases with refined providers,” Prodaft wrote. “Their method marks a brand new period in underground enterprise practices, emphasizing scalability and effectivity in cybercriminal operations.”
A new report from researchers on the safety agency SilentPush finds the Smishing Triad members have expanded into promoting cell phishing kits focusing on prospects of worldwide monetary establishments like CitiGroup, MasterCard, PayPal, Stripe, and Visa, in addition to banks in Canada, Latin America, Australia and the broader Asia-Pacific area.

Phishing lures from the Smishing Triad spoofing PayPal. Picture: SilentPush.
SilentPush discovered the Smishing Triad now spoofs recognizable manufacturers in a wide range of trade verticals throughout at the very least 121 international locations and an unlimited variety of industries, together with the postal, logistics, telecommunications, transportation, finance, retail and public sectors.
In line with SilentPush, the domains utilized by the Smishing Triad are rotated incessantly, with roughly 25,000 phishing domains lively throughout any 8-day interval and a majority of them sitting at two Chinese language internet hosting corporations: Tencent (AS132203) and Alibaba (AS45102).
“With almost two-thirds of all international locations on the earth focused by [the] Smishing Triad, it’s protected to say they’re primarily focusing on each nation with fashionable infrastructure outdoors of Iran, North Korea, and Russia,” SilentPush wrote. “Our workforce has noticed some potential focusing on in Russia (resembling domains that talked about their nation codes), however nothing definitive sufficient to point Russia is a persistent goal. Curiously, although these are Chinese language risk actors, now we have seen cases of focusing on aimed toward Macau and Hong Kong, each particular administrative areas of China.”
SilentPush’s Zach Edwards mentioned his workforce discovered a vulnerability that uncovered knowledge from one of many Smishing Triad’s phishing pages, which revealed the variety of visits every web site acquired every day throughout 1000’s of phishing domains that have been lively on the time. Based mostly on that knowledge, SilentPush estimates these phishing pages acquired nicely greater than 1,000,000 visits inside a 20-day time span.
The report notes the Smishing Triad boasts it has “300+ entrance desk workers worldwide” concerned in considered one of their extra fashionable phishing kits — Lighthouse — workers that’s primarily used to help varied points of the group’s fraud and cash-out schemes.
The Smishing Triad members preserve their very own Chinese language-language gross sales channels on Telegram, which incessantly provide movies and pictures of their workers laborious at work. A few of these photos embrace huge partitions of telephones used to ship phishing messages, with human operators seated instantly in entrance of them able to obtain any time-sensitive one-time codes.
As famous in February’s story How Phished Data Turns Into Apple and Google Wallets, a kind of cash-out schemes includes an Android app referred to as Z-NFC, which might relay a sound NFC transaction from considered one of these compromised digital wallets to anyplace on the earth. For a $500 month subscription, the client can wave their telephone at any fee terminal that accepts Apple or Google pay, and the app will relay an NFC transaction over the Web from a stolen pockets on a telephone in China.
Chinese language nationals have been not too long ago busted attempting to make use of these NFC apps to purchase high-end electronics in Singapore. And in the USA, authorities in California and Tennessee arrested Chinese nationals accused of using NFC apps to fraudulently buy present playing cards from retailers.
The Prodaft researchers mentioned they have been capable of finding a beforehand undocumented backend administration panel for Lucid, a smishing-as-a-service operation tied to the XinXin Group. The panel included sufferer figures that recommend the smishing campaigns preserve a median success charge of roughly 5 p.c, with some domains receiving over 500 visits per week.
“In a single noticed occasion, a single phishing web site captured 30 bank card information from 550 sufferer interactions over a 7-day interval,” Prodaft wrote.
Prodaft’s report particulars how the Smishing Triad has achieved such success in sending their spam messages. For instance, one phishing vendor seems to ship out messages utilizing dozens of Android machine emulators operating in parallel on a single machine.
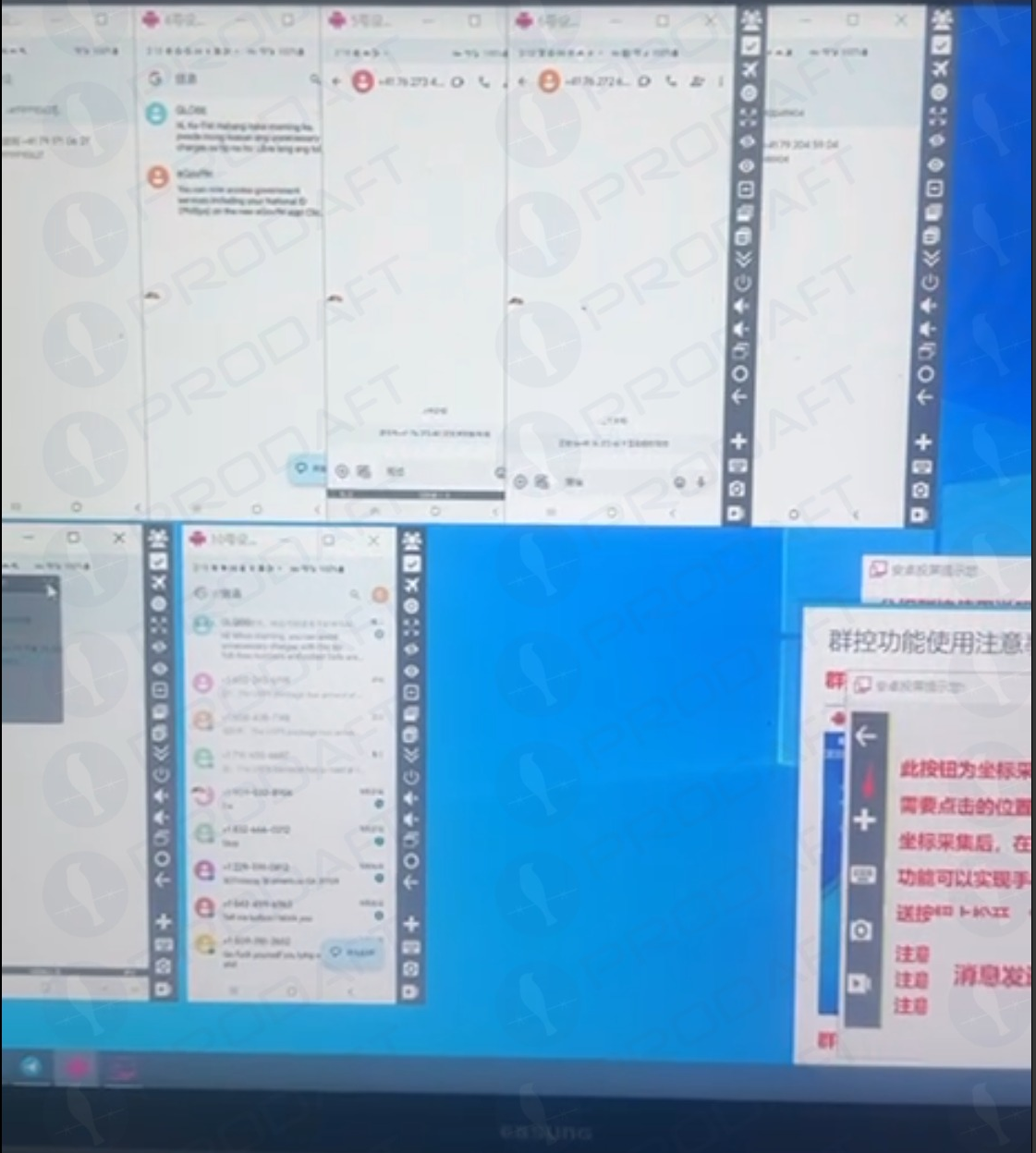
Phishers utilizing a number of virtualized Android gadgets to orchestrate and distribute RCS-based rip-off campaigns. Picture: Prodaft.
In line with Prodaft, the risk actors first purchase telephone numbers via varied means together with knowledge breaches, open-source intelligence, or bought lists from underground markets. They then exploit technical gaps in sender ID validation inside each messaging platforms.
“For iMessage, this includes creating momentary Apple IDs with impersonated show names, whereas RCS exploitation leverages provider implementation inconsistencies in sender verification,” Prodaft wrote. “Message supply happens via automated platforms utilizing VoIP numbers or compromised credentials, typically deployed in exactly timed multi-wave campaigns to maximise effectiveness.
As well as, the phishing hyperlinks embedded in these messages use time-limited single-use URLs that expire or redirect primarily based on machine fingerprinting to evade safety evaluation, they discovered.
“The economics strongly favor the attackers, as neither RCS nor iMessage messages incur per-message prices like conventional SMS, enabling high-volume campaigns at minimal operational expense,” Prodaft continued. “The overlap in templates, goal swimming pools, and techniques amongst these platforms underscores a unified risk panorama, with Chinese language-speaking actors driving innovation within the underground economic system. Their skill to scale operations globally and evasion strategies pose important challenges to cybersecurity defenses.”
Ford Merrill works in safety analysis at SecAlliance, a CSIS Security Group firm. Merrill mentioned he’s noticed at the very least one video of a Home windows binary that wraps a Chrome executable and can be utilized to load in goal telephone numbers and blast messages by way of RCS, iMessage, Amazon, Instagram, Fb, and WhatsApp.
“The proof we’ve noticed suggests the power for a single machine to ship roughly 100 messages per second,” Merrill mentioned. “We additionally consider that there’s functionality to supply nation particular SIM playing cards in quantity that permit them to register totally different on-line accounts that require validation with particular nation codes, and even make these SIM playing cards obtainable to the bodily gadgets long-term in order that providers that depend on checks of the validity of the telephone quantity or SIM card presence on a cell community are thwarted.”
Specialists say this fast-growing wave of card fraud persists as a result of far too many monetary establishments nonetheless default to sending one-time codes by way of SMS for validating card enrollment in cell wallets from Apple or Google. KrebsOnSecurity interviewed a number of safety executives at non-U.S. monetary establishments who spoke on situation of anonymity as a result of they weren’t approved to talk to the press. These banks have since executed away with SMS-based one-time codes and are actually requiring prospects to log in to the financial institution’s cell app earlier than they will hyperlink their card to a digital pockets.















