Microsoft has revealed the existence of a brand new North Korean risk actor, dubbed Moonstone Sleet.
Beforehand tracked as Storm-1789, a denomination utilized by the tech large for uncategorized malicious exercise clusters, Moonstone Sleet has been energetic since not less than early August 2023.
Till now, the risk actor demonstrated substantial overlaps with Diamond Sleet, one other North Korean group.
“[Moonstone Sleet] was extensively reusing code from recognized Diamond Sleet malware like Comebacker and utilizing well-established Diamond Sleet strategies to realize entry to organizations, comparable to utilizing social media to ship trojanized software program,” Microsoft defined of their report revealed on Could 28.
Overlaps are widespread throughout the North Korean risk panorama, within which nearly all risk teams work for a similar trigger: serving the regime. This leads some cyber risk intelligence researchers to attribute any malicious exercise from a North Korean group to the umbrella group Lazarus.
Moonstone Sleet’s Methods, Techniques and Procedures
Moonstone Sleet has shifted to its personal bespoke infrastructure and assaults, prompting Microsoft to attribute the group a singular title.
To compromise its victims’ IT methods, Moonstone Sleet employs a mix of tried-and-tested and new strategies, together with organising faux corporations and job alternatives to interact with potential targets, deploying trojanized variations of reputable instruments and creating malicious video games.
The group additionally delivers its personal customized ransomware.
Trojanized Reliable Instruments
One of many earliest Moonstone Sleet methods detected by Microsoft dates again to August 2023, when the risk actor was noticed delivering a trojanized model of PuTTY, an open-source terminal emulator, by way of apps like LinkedIn and Telegram in addition to developer freelancing platforms.
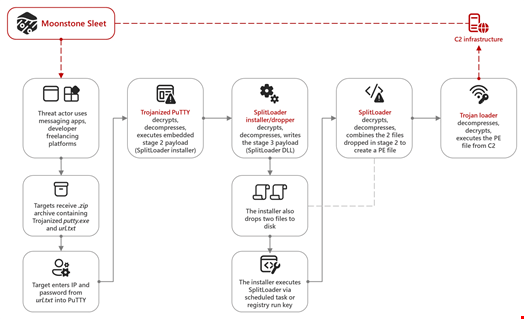
Equally, the group focused potential victims with initiatives that used malicious npm packages, usually via freelancing web sites or different platforms like LinkedIn.
This use of widespread social media platforms to ship malicious payloads has been noticed with different North Korean actors like Diamond Sleet.
Faux Firms
From January 2024, Moonstone Sleet was noticed creating a number of faux corporations impersonating software program improvement and IT providers, sometimes referring to blockchain and AI.
StarGlow Ventures and C.C. Waterfall have been two examples of corporations created by the group to succeed in potential targets.
The group used a mix of created web sites and social media accounts so as to add legitimacy to their campaigns.
Malicious Recreation
In February 2024, Moonstone Sleet added a malicious cell tank-themed recreation it developed to its hacking portfolio.
The sport has a number of names, together with DeTankWar, DeFiTankWar, DeTankZone, and TankWarsZone.
“On this marketing campaign, Moonstone Sleet sometimes approaches its targets via messaging platforms or by electronic mail, presenting itself as a recreation developer searching for funding or developer help and both masquerading as a reputable blockchain firm or utilizing faux corporations,” Microsoft wrote.
FakePenny Ransomware
Lastly, in April 2024, Microsoft detected that Moonstone Sleet had began delivering a brand new customized ransomware variant, which the tech large named FakePenny.
The ransomware features a loader and an encryptor. The ransomware observe dropped by FakePenny intently overlaps with the observe utilized by Seashell Blizzard in its malware NotPetya.
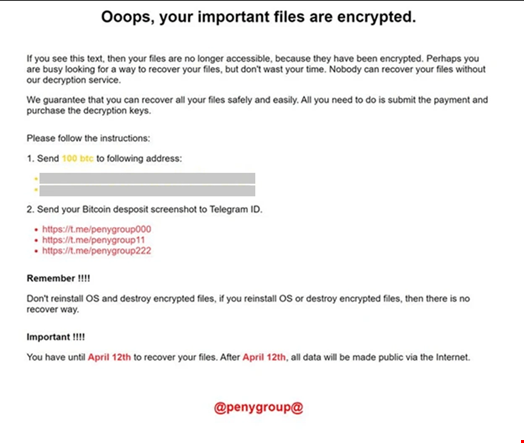
One ransom demand the group sought from a compromised firm was $6.6m in Bitcoin, which is considerably larger than ransom calls for for different North Korean ransomware, comparable to WannaCry 2.0 and H0lyGh0st.













